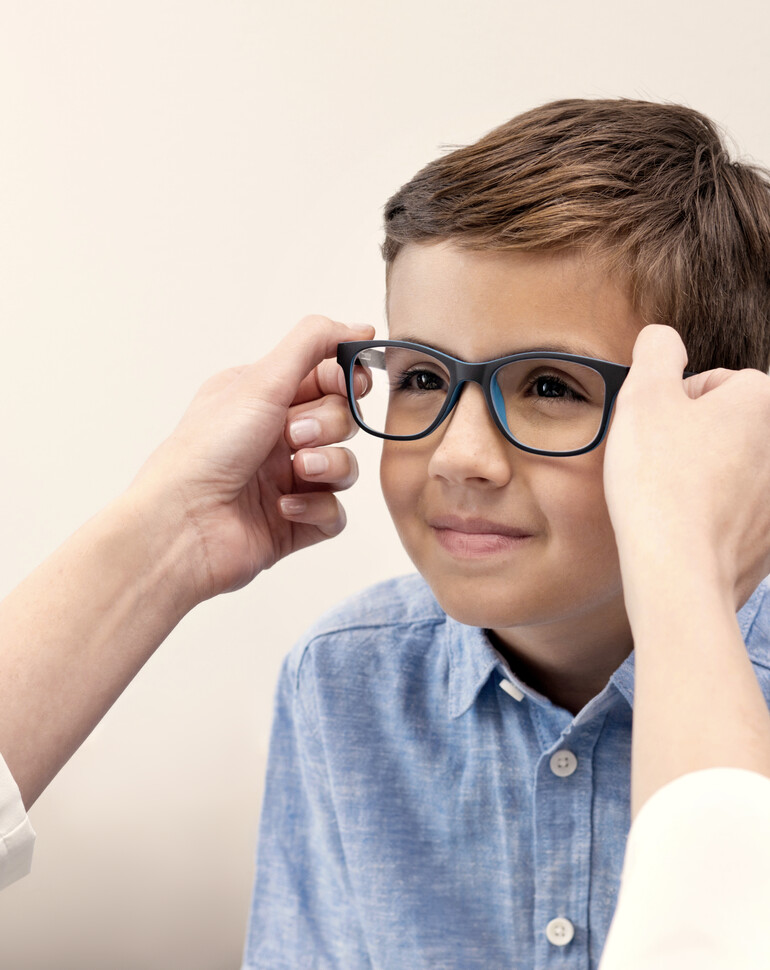
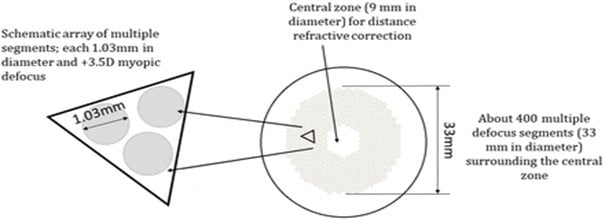
Prohlášení o odmítnutí odpovědnosti: Čočky MiYOSMART nejsou schválené pro úpravu myopie ve všech zemích, včetně Spojených států amerických, a tudíž v současné době nejsou dostupné k prodeji ve všech zemích, včetně Spojených států amerických.
Odkazy:
1. Bělíková J. Vývoj myopie, 1.část. Česká oční optika. 4, 2012, Sv. 53.
2. Holden BA, Fricke TR, Wilson DA, Jong M, Naidoo KS, Sankaridurg P, Wong TY, Naduvilath TJ, Resnikoff S. Global Prevalence of Myopia and High Myopia and Temporal Trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology. 123, 2016, Sv. 5.
3. Fricke TR, Holden BA, Wilson DA, et al. Global cost of correcting vision impairment from uncorrected refractive error. Bulletin of the World Health Organisation. 90, 2012, Sv. 10.
4. https://www.hoyavision.com/cz/opticke-vyrobky/miyosmart/ (dostupné online).
5. Lam CSY, Tang WC, Tse DY, et al Defocus Incorporated Multiple Segments (DIMS) spectacle lenses slow myopia progression: a 2-year randomised clinical trial British Journal of Ophthalmology 2020;104:363-368.
6. Donovan L, Sankaridurg P, Ho A, et al. Myopia progression rates in urban children wearing single-vision spectacles. Optom Vis Sci 2012; 89:27–32.
7. Huang HM, Chang DS, Wu PC. The Association between Near Work Activities and Myopia in Children-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015 Oct 20;10(10):e0140419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140419. PMID: 26485393; PMCID: PMC4618477.
8. Wen L, Cao Y, Cheng Q, Li X, Pan L, Li L, Zhu H, Lan W, Yang Z. Objectively measured near work, outdoor exposure and myopia in children. Br J Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov;104(11):1542-1547.
9. Li SM, Li SY, Kang MT, Zhou Y, Liu LR, Li H, Wang YP, Zhan SY, Gopinath B, Mitchell P, Wang N; Anyang Childhood Eye Study Group. Near Work Related Parameters and Myopia in Chinese Children: the Anyang Childhood Eye Study. PLoS One. 2015 Aug 5;10(8):e0134514.
10. Jones LA, Sinnott LT, Mutti DO, et al. Parental history of myopia, sports and outdoor activities, and future myopia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:3524–3532.
11. Rose KA, Morgan IG, Ip J, et al. Outdoor activity reduces the prevalence of myopia in children. Ophthalmology.2008;115:1279–1285.
12. Xiong S, Sankaridurg P, Naduvilath T, Zang J, Zou H, Zhu J, Lv M, He X, Xu X. Time spent in outdoor activities in relation to myopia prevention and control: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017 Sep;95(6):551-566.
13. Wang J, Li Y, Musch DC, Wei N, Qi X, Ding G, Li X, Li J, Song L, Zhang Y, Ning Y, Zeng X, Hua N, Li S, Qian X. Progression of Myopia in School-Aged Children After COVID-19 Home Confinement. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar 1;139(3):293-300.
14. Hu Y, Zhao F, Ding X, Zhang S, Li Z, Guo Y, Feng Z, Tang X, Li Q, Guo L, Lu C, Yang X, He M. Rates of Myopia Development in Young Chinese Schoolchildren During the Outbreak of COVID-19. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2021 Oct 1;139(10):1115-1121.
15. Ma M, Xiong S, Zhao S, Zheng Z, Sun T, Li C. COVID-19 Home Quarantine Accelerated the Progression of Myopia in Children Aged 7 to 12 Years in China. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Aug 2;62(10):37. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.10.37. PMID: 34463719; PMCID: PMC8411864.
16. Jin, E., Lee, C.E., Li, H. et al. Association between sleep and myopia in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2023).
17. Jee D, Morgan IG, Kim EC. Inverse relationship between sleep duration and myopia. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016;94(3):e204-e210. doi:10.1111/aos.12776.
18. French AN, Ashby RS, Morgan IG, et al. Time outdoors and the prevention of myopia. Exp Eye Res 2013; 114: 58–68.
19. Zakova M, Fus M, Tejkl L. Efficacy of Spectacle Correction Using Defocus Incorporated Multiple Segments in the Myopic Population. Clin Ophthalmol. 2025;19:3191-3199, https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S541232.